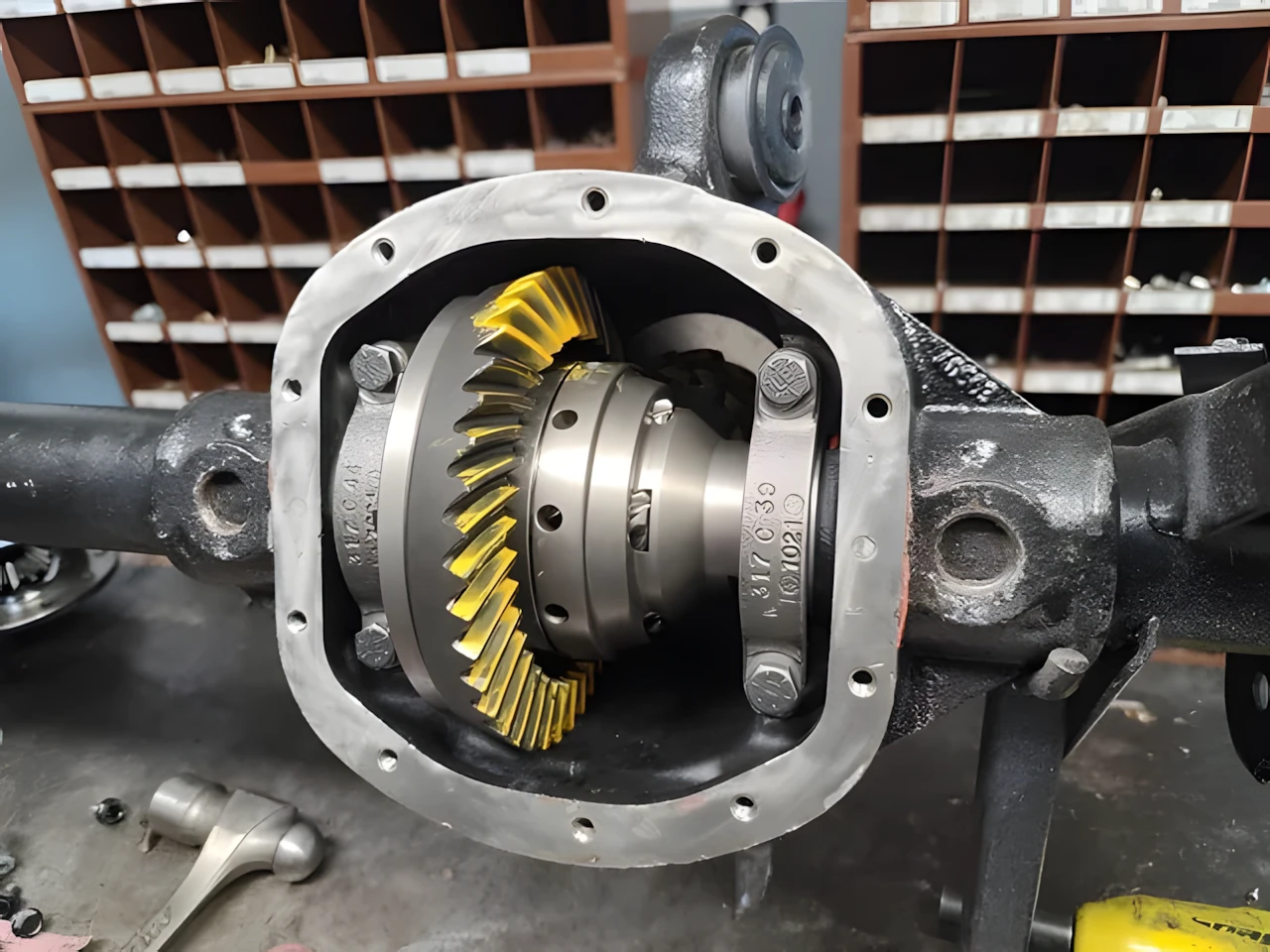
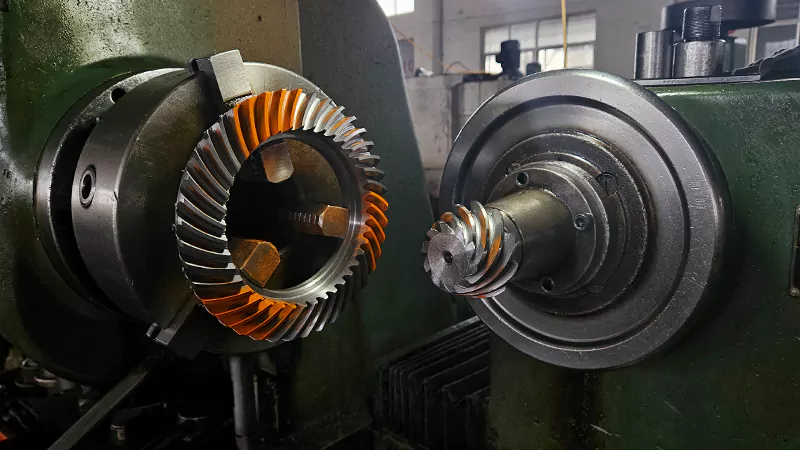
Ring and pinion gears are critical components of a vehicle’s drivetrain, responsible for transferring power from the driveshaft to the wheels. These gears are typically found in the differential, a key part of the axle assembly. Here’s an explanation of how they work:
Basic Function
The primary job of the ring and pinion gears is to translate the rotational motion from the driveshaft into the rotational motion needed to turn the wheels. At the same time, they provide a gear reduction, enabling the vehicle to manage torque and speed efficiently.
Components and Setup
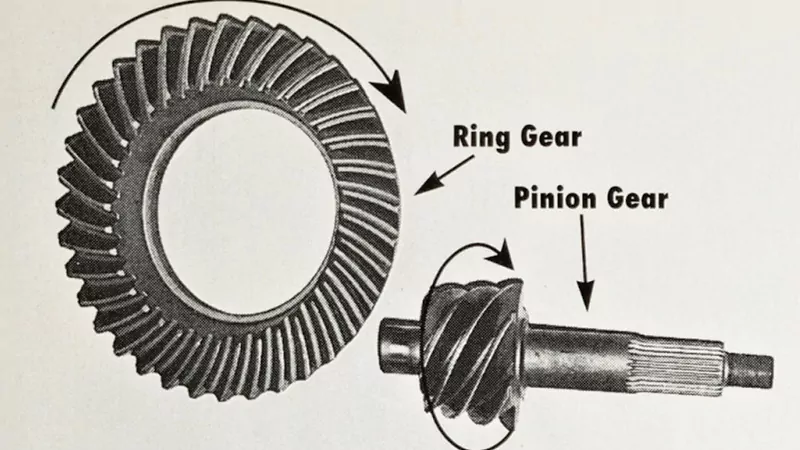
- Pinion Gear: A smaller gear connected to the driveshaft. It rotates at high speed and drives the ring gear.
- Ring Gear: A larger gear mounted to the differential case. It transfers power to the axle shafts, which then turn the wheels.
The pinion gear meshes with the ring gear at an angle, typically forming a hypoid or spiral bevel gear set. This design ensures smooth and efficient power transfer while managing the directional change of motion.
Gear Ratio
The ratio between the number of teeth on the ring gear and the pinion gear is called the gear ratio. For example, if the ring gear has 41 teeth and the pinion has 10, the ratio is 4.10:1.
- Higher Ratios (e.g., 4.56:1): Provide more torque at the wheels but reduce top speed. Ideal for off-road or towing applications.
- Lower Ratios (e.g., 3.23:1): Provide higher speeds but less torque. Suitable for highway driving.
Precision and Adjustments
For optimal performance, ring and pinion gears must be installed with precise alignment. Key aspects include:
- Backlash: The slight gap between the teeth of the ring and pinion gears. Proper backlash ensures smooth engagement and minimizes noise.
- Pinion Depth: The position of the pinion gear relative to the ring gear. This alignment affects load distribution and gear longevity.
- Bearing Preload: Ensures the gears and bearings remain tightly secured without excessive friction.
Importance of Maintenance
To ensure longevity and performance:
- Regular Oil Changes: Use the manufacturer-recommended gear oil and replace it at the specified intervals.
- Inspections: Periodically check for wear, noise, or excessive play in the gears.
- Proper Installation: Always rely on professionals or follow detailed procedures when installing new ring and pinion gears.
Conclusion
Ring and pinion gears are the backbone of a vehicle’s drivetrain, enabling efficient power delivery and adaptability to diverse driving conditions. Their precise design and operation ensure that vehicles can tackle both everyday roads and challenging terrains with ease. Understanding their workings highlights their role in shaping a vehicle’s performance, reliability, and versatility.



