Choosing the correct differential gear ratio is crucial for enhancing your vehicle’s performance. The right gear ratio not only optimizes acceleration but also impacts fuel efficiency and top speed. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamentals of differential gear ratios and how to calculate them, helping you make the best choice for your vehicle.
What Is a Gear Ratio?
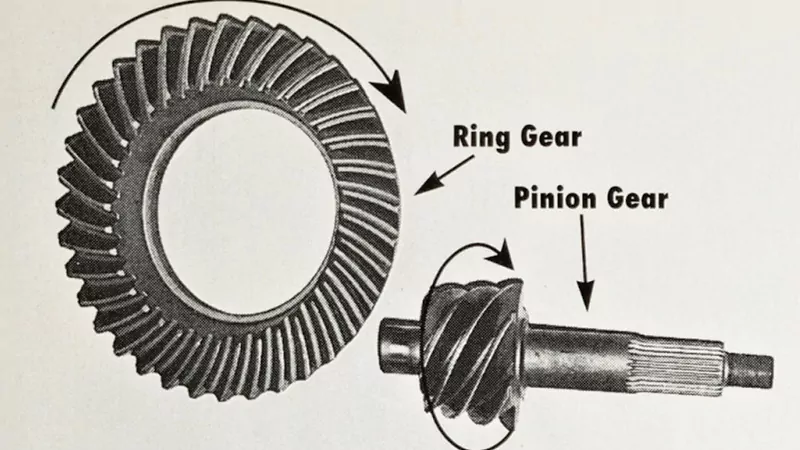
Simply put, a differential gear ratio refers to the ratio between the number of teeth on the ring gear and the pinion gear. This ratio determines how engine power is transmitted through the drivetrain to the wheels.
When the pinion gear rotates at a specific input speed, it drives the larger ring gear. This motion reduces output speed but increases torque, which is essential for vehicle performance.
The formula for calculating the gear ratio is:
Gear Ratio = Number of Ring Gear Teeth ÷ Number of Pinion Gear Teeth
For example, if a pinion gear has 10 teeth and the ring gear has 41 teeth, the gear ratio would be 4.1. This means that for every full rotation of the ring gear, the pinion gear rotates 4.1 times, effectively multiplying the input torque by 4.1.
How Gear Ratios Impact Vehicle Performance
Gear ratios play a critical role in a vehicle’s acceleration, fuel efficiency, and top speed.
Acceleration Performance
A higher gear ratio (e.g., 4.10:1) amplifies the engine’s torque, delivering more power to the wheels. This setup is ideal for applications requiring rapid acceleration and strong initial pull, such as street racing or towing competitions. A high gear ratio helps the vehicle overcome inertia quickly, making it accelerate faster. However, this also means the engine will reach higher RPMs at lower speeds, potentially increasing engine noise and fuel consumption—especially in stop-and-go traffic or city driving.
Fuel Efficiency
On the other hand, a lower gear ratio (e.g., 3.08:1) is more beneficial for highway cruising. It allows the engine to maintain a lower RPM while keeping a consistent speed, reducing fuel consumption. For long-distance travel and highway driving, a lower gear ratio improves fuel efficiency, minimizes engine wear, and provides a smoother driving experience. Additionally, lower gear ratios keep engine noise levels down during steady cruising, making them a great choice for daily commutes and road trips.
Top Speed
Gear ratios also impact a vehicle’s top speed. A lower gear ratio enables the engine to continue accelerating without hitting the redline too quickly, allowing for higher top speeds. This is because a lower ratio lets the engine generate sufficient power at lower RPMs while extending shift points, leading to higher wheel speeds. Conversely, a higher gear ratio, while beneficial for acceleration, causes the engine to reach its maximum RPM too quickly, limiting high-speed performance. Therefore, for vehicles focused on top speed and highway stability, a lower gear ratio is often the better choice.

How Tire Size Affects Gear Ratios
Tire size plays a crucial role in a vehicle’s drivetrain and overall performance. Even if the differential gear ratio remains unchanged, altering tire size can significantly impact how a vehicle behaves.
- Larger Tire Diameter: Larger tires cover more ground per revolution, effectively lowering the gear ratio. As a result, the engine operates at a lower RPM, which may reduce acceleration response and weaken power output.
- Smaller Tire Diameter: Smaller tires travel a shorter distance per revolution, effectively increasing the gear ratio. This leads to higher engine RPM at the same speed, improving acceleration but potentially increasing fuel consumption and engine noise at highway speeds.
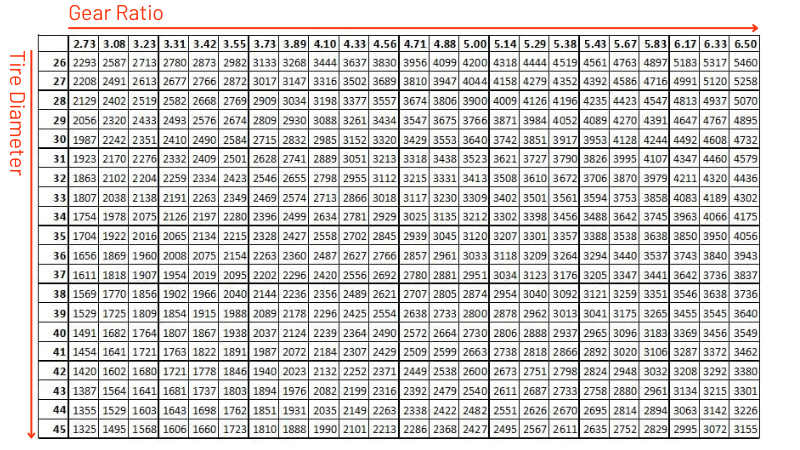
To better understand these effects, you can use the following formula to calculate engine RPM:
RPM=(MPH×Gear Ratio×336)/Tire Diameter
Formula Breakdown:
- MPH (Miles Per Hour): The vehicle’s speed—higher speeds result in higher engine RPM.
- Gear Ratio: Determines how engine torque is multiplied; a higher ratio increases RPM at the same speed.
- 336: A constant used for unit conversion, ensuring accurate RPM calculations.
- Tire Diameter (in inches): A larger diameter reduces RPM at a given speed, while a smaller diameter increases it.
When changing tires, it’s important to consider not only aesthetics and traction but also how the new size affects the gear ratio. Adjusting the gear ratio accordingly ensures optimal acceleration, fuel efficiency, and top speed. Choosing the right combination of tire size and gear ratio will help maintain a balanced driving experience, optimizing both performance and economy.
Differential Gear Ratio Calculator
Gear Ratio Formula: (RPM × Tire Diameter) ÷ (MPH × 336)
How to choose the right gear ration?
Selecting the optimal gear ratio is crucial for balancing vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, and driving experience. When determining the best gear ratio, consider the following factors:
1. Driving Needs
Your primary driving conditions and requirements should guide your choice, as different gear ratios affect acceleration, fuel efficiency, and cruising speed in various ways.
- Prioritizing Acceleration: A higher gear ratio (e.g., 4.10:1 or higher) enhances low-speed acceleration and towing power, making it ideal for off-road vehicles, towing applications, or drag racing.
- Maximizing Fuel Efficiency: A lower gear ratio (e.g., 3.08:1 or lower) reduces engine RPM, improving fuel economy—best suited for highway driving and daily commuting.
- Balanced Performance: If you want both decent acceleration and efficient highway cruising, a mid-range gear ratio (e.g., 3.55:1 or 3.73:1) offers a compromise.
2. Engine Characteristics
Every engine has an optimal RPM range where it delivers the best torque and power. Choosing the right gear ratio helps keep the engine operating within this range.
- High-Torque, Low-Revving Engines (e.g., Large V8s): A lower gear ratio improves fuel economy by maintaining lower RPMs.
- High-Revving, Small-Displacement Engines: A higher gear ratio helps the engine reach its power band more quickly, improving acceleration.
- Turbocharged Engines: Since turbochargers operate best within specific RPM ranges, the gear ratio should help keep the engine within that boost range.
3. Vehicle Application
Different vehicle types and driving purposes require different gear ratios.
- Daily Driving: Low to mid-range ratios (e.g., 3.23:1, 3.55:1) offer a good balance of acceleration and fuel efficiency.
- Highway Cruising: Lower gear ratios (e.g., 2.73:1, 3.08:1) keep engine RPMs low, improving fuel economy and reducing noise and wear.
- Towing & Heavy Loads: Higher gear ratios (e.g., 4.10:1 or higher) provide increased torque for hauling trailers and heavy cargo.
- Performance & Racing: Very high gear ratios (e.g., 4.56:1, 4.88:1) improve acceleration, making them ideal for drag racing or track performance.
- Off-Roading: High gear ratios (e.g., 4.10:1 or higher) enhance low-speed torque for better climbing and rough-terrain maneuverability.
Summary
When selecting a gear ratio, the key is to find the right balance between your driving style, vehicle application, and engine characteristics.
- If you primarily drive on highways, a lower gear ratio improves fuel efficiency by keeping engine RPMs lower.
- If you prioritize acceleration or towing power, a higher gear ratio enhances torque and performance.
Choosing the right gear ratio not only improves your driving experience but also optimizes fuel economy and power output, ensuring your vehicle performs efficiently in its intended application.