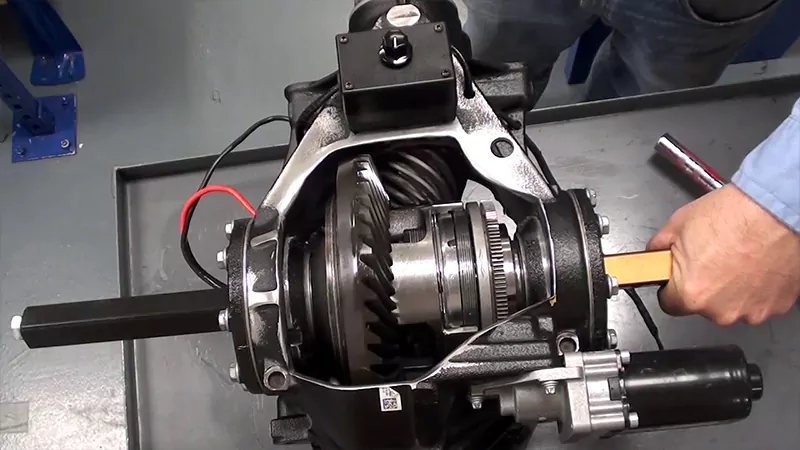
In the world of agricultural machinery, efficiency, durability, and precision are not just desirable—they are absolutely necessary. One component that plays a significant role in making all of this possible is the ring and pinion gear system. These gears are responsible for the crucial task of transferring torque between differentials and axles, ensuring that power is transmitted smoothly to the wheels, which is essential for high-performance machinery. From tractors to harvesters, ring and pinion gears are fundamental to the seamless operation of agricultural equipment, especially when dealing with challenging terrain and heavy-duty work.

What Exactly Are Ring and Pinion Gears and How Do They Work?
At its core, the ring and pinion gear system consists of two bevel gears—one large and one small. The pinion gear, located on the smaller axle, engages with the ring gear, which has a larger diameter and is attached to the main drive axle. This arrangement allows torque from the engine to be transferred to the wheels at a 90-degree angle.
The pinion typically has fewer teeth than the ring gear, and together they work as a pair to distribute torque efficiently. The ratio between the number of teeth on the ring and pinion gear determines the overall gear ratio, which directly affects the machinery’s performance. A higher ratio provides more torque for heavy-duty tasks like plowing, while a lower ratio can offer better fuel efficiency for less demanding tasks.
The Importance of Ring and Pinion Gears in Agricultural Applications
Efficient Power Delivery in Challenging Conditions
Agricultural machinery often works in challenging conditions—wet, muddy, hilly, and uneven terrains. This places immense strain on the powertrain, which has to handle both heavy loads and diverse working environments. Ring and pinion gears are crucial for transferring engine power with minimal loss. Their design ensures that power is distributed evenly to the wheels, which allows the machine to maintain traction and stability, even in difficult conditions.
For example, when tractors are used for plowing fields, they must exert substantial force to break the soil. In such high-load scenarios, ring and pinion gears ensure that the machine operates efficiently without loss of power, preventing unnecessary slippage and strain on the engine.
Enhancing Durability and Longevity
The harsh working environments of farms demand high durability from all components. Ring and pinion gears used in agricultural machinery are often made from high-strength steel alloys, engineered to withstand the repeated stresses of heavy-duty operations. In addition, these gears undergo specialized heat treatment processes such as carburizing (hardening the surface) or induction hardening to increase their resistance to wear and fatigue. This helps maintain the machinery’s performance over long periods, even when exposed to dirt, moisture, and high torque.
Versatility Across Different Agricultural Machines
Ring and pinion gears are not one-size-fits-all. The diversity of agricultural tasks, from tilling and planting to harvesting and hauling, requires a variety of gear ratios to match the specific needs of the machine. Different types of agricultural machinery—tractors, combine harvesters, sprayers, and more—use ring and pinion gears, but the exact specifications can vary widely.
For instance, tractors used for heavy-duty work, such as plowing or hauling, often require higher gear ratios that maximize torque and power delivery, whereas combine harvesters might use gears designed for speed and efficiency in low-resistance conditions. Ring and pinion gears play a critical role in customizing the drivetrain to match the unique demands of each machine.
Challenges and Maintenance
While ring and pinion gears are durable, their performance is still highly dependent on proper maintenance. Regular checks for gear wear, alignment, and lubrication can prevent unnecessary damage. Advanced lubrication systems are critical for keeping the gears running smoothly and minimizing friction, which extends the lifespan of the gears and improves the overall efficiency of the machinery.
Moreover, keeping the gear system clean and free from contaminants is essential. Dirt and debris can cause wear over time, leading to costly repairs or replacements. Farmers must follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for servicing intervals and lubricants to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
Ring and pinion gears remain a critical component in the design and operation of agricultural machinery. As technology continues to advance, these gears are evolving to become more durable, efficient, and customizable to meet the increasing demands of modern farming. Whether you’re in charge of maintaining a fleet of machines or designing new agricultural equipment, understanding the intricacies of ring and pinion gears is essential for achieving optimal performance and longevity.
In the future, innovations in materials, manufacturing precision, and gear customization will continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in agricultural machinery. By embracing these advancements, farmers can look forward to more powerful, efficient, and durable equipment, ultimately improving productivity in the agricultural industry.