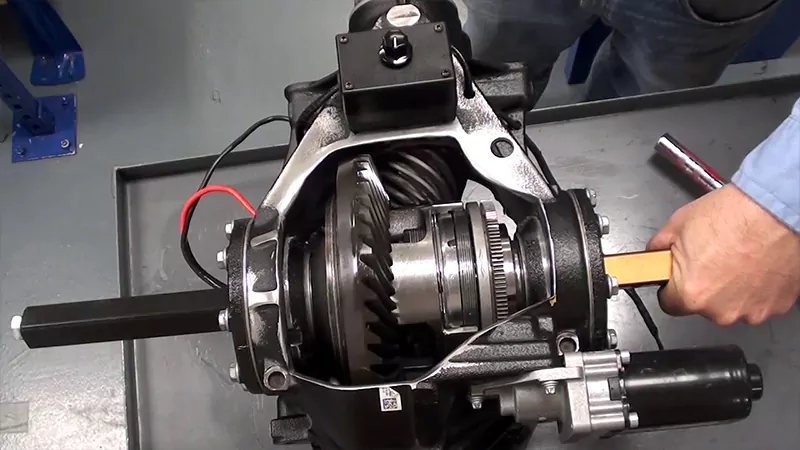
The crown wheel and pinion ratio, commonly referred to as the gear ratio in automotive terms, is a critical specification that determines how torque is transmitted from the engine to the wheels through the drivetrain. This ratio is essential for understanding a vehicle’s performance, fuel efficiency, and overall driving experience.

Understanding the Basics
In a car’s drivetrain, the crown wheel and pinion are integral components of the differential. The pinion gear, connected to the driveshaft, engages with the larger crown wheel inside the differential housing. Together, they transfer power from the engine to the wheels.
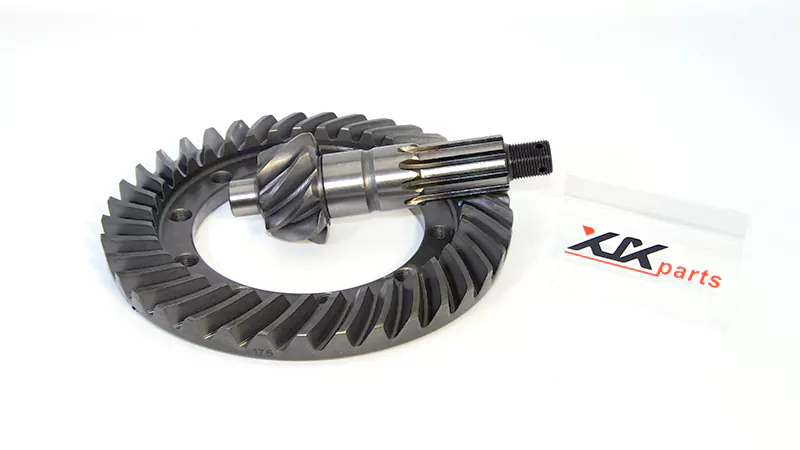
The ratio between the number of teeth on the crown wheel and the pinion gear defines the crown wheel and pinion ratio. For example:
- If the crown wheel has 41 teeth and the pinion has 10 teeth, the gear ratio is 4.10:1.
- If the crown wheel has 37 teeth and the pinion has 9 teeth, the gear ratio is 4.11:1.
These are common ratios found in vehicles designed for off-road or heavy-duty purposes. The ratio indicates how many times the pinion must rotate to make the crown wheel complete one full rotation.
Why Does the Ratio Matter?
The gear ratio significantly impacts a vehicle’s performance. Here’s how:
Acceleration vs. Top Speed
- Lower Ratio (e.g., 3.55:1): The vehicle achieves higher top speeds but accelerates more slowly. This is ideal for sports cars or vehicles used on highways.
- Higher Ratio (e.g., 4.10:1): The vehicle accelerates faster but has a lower top speed. Such configurations are common in off-road or heavy-duty vehicles where torque is crucial.
Fuel Efficiency
A lower ratio often results in better fuel economy, as the engine operates at lower RPMs during cruising speeds. However, vehicles with a higher ratio may consume more fuel due to increased engine workload.
Towing and Off-Roading
Vehicles designed for towing or off-road use typically have a higher gear ratio. This provides the necessary torque to move heavy loads or navigate challenging terrains.
Applications in Different Vehicles
Sports Cars
Sports cars often have a balanced ratio that allows for quick acceleration without sacrificing top speed. For example, ratios like 3.73:1 or 3.91:1 are common and well-suited for their high-performance engines.
Off-Road Vehicles
Off-road vehicles prioritize high torque over speed, which is why they use higher ratios such as 4.56:1 or even 4.88:1. This ensures the wheels can maintain traction on uneven or slippery surfaces.
Commercial Trucks
Trucks designed for heavy loads typically feature high gear ratios like 4.10:1 or 4.33:1 to maximize pulling power, especially when climbing hills or hauling cargo.
How to Identify Your Vehicle’s Gear Ratio
The crown wheel and pinion ratio is usually specified in the vehicle’s owner’s manual or on a label located on the differential housing. Some aftermarket modifications, such as upgrading to larger tires, may require adjusting the gear ratio to maintain optimal performance.
Conclusion
The crown wheel and pinion ratio is more than just a technical detail; it’s a key factor in determining how a vehicle performs under different conditions. Whether you’re seeking better fuel economy, faster acceleration, or enhanced towing capability, understanding this ratio is essential. By choosing the right configuration for your needs, you can ensure your vehicle delivers the performance you desire.