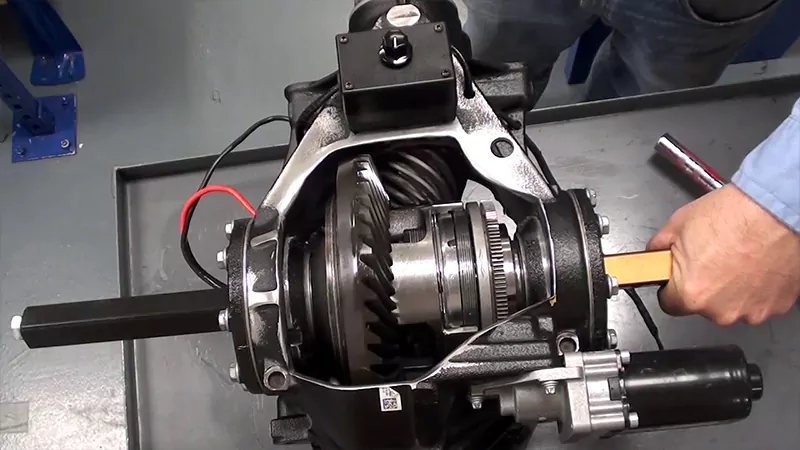
As an important component in the transmission system, the manufacturing process of the horn gear not only requires high precision and high quality, but also needs to ensure its stability and durability under harsh working conditions. This article will discuss in detail the various processing links of the horn gear from material selection to the final product.

Material Selection
The manufacturing materials for ring and pinion gears are typically high-strength, wear-resistant steels. These materials offer excellent mechanical properties and heat treatment capabilities, ensuring that the gears can meet the demands of complex operating conditions.
Forging Process
Cutting and Heating
According to the design drawings of the ring and pinion gears, raw materials are cut into suitable sizes and shapes using cutting equipment. The cut materials are then heated in a furnace to the forging temperature. The temperature and time during heating need to be strictly controlled to ensure that the material has good plasticity and low deformation resistance during forging.
Forging
The heated raw materials are sent to a forging press or hammer for shaping. During forging, operators need to adjust the forging equipment parameters, such as forging force and speed, according to the shape and size of the forging. Through multiple forging and shaping steps, the raw material gradually takes on the preliminary shape of the ring and pinion gears. After forging, the forged parts must be trimmed to remove excess burrs and flash.
Heat Treatment
The forged ring and pinion gears require heat treatment to improve hardness and wear resistance. Quenching involves rapidly cooling the forged parts to below room temperature to induce a phase change in the internal structure, increasing hardness and strength. However, quenching can also induce significant internal stresses, so tempering is necessary to relieve these stresses and stabilize the structure. Tempering involves heating the quenched parts to a specific temperature and holding them there to allow for stress relief and recrystallization, achieving the desired mechanical properties and toughness.
Machining
Rough Machining
After heat treatment, the ring and pinion gears undergo rough machining to remove excess material from the forging process and initially form their final shape. Rough machining is typically done on lathes, milling machines, and other machine tools to remove extra material and achieve certain dimensional precision and surface roughness.
Finishing Machining
Building on rough machining, finishing machining is performed to ensure precise dimensions and surface quality. This includes processes such as gear surface grinding and gear shape correction. Surface grinding uses a grinder to achieve precision and smoothness of the gear surfaces, while shape correction involves adjusting machine parameters and tool shapes to correct gear shape errors and spacing deviations. The finished ring and pinion gears will have higher dimensional accuracy and surface quality, meeting stricter usage requirements.
Inspection and Assembly
Inspection
Comprehensive inspection of the finished ring and pinion gears is crucial to ensure they meet design requirements. Inspection includes dimensional measurements, geometric tolerance checks, and hardness tests. Advanced measuring equipment and methods are used to accurately measure and evaluate the performance indicators of the ring and pinion gears to ensure they meet relevant standards and specifications.
Assembly
The inspected and approved ring and pinion gears are assembled with other transmission components to form a complete transmission system. During assembly, the accuracy of the fit and gaps between parts must be ensured, and the operation and performance of the transmission system should be checked to ensure proper functioning and compliance with usage requirements.
Conclusion
The manufacturing process of ring and pinion gears is complex and precise, involving multiple stages and knowledge from various technical fields. Through strict quality control and detailed craftsmanship, it ensures that ring and pinion gears exhibit excellent performance and quality, meeting the requirements for various complex operating conditions. With ongoing advancements in manufacturing technology and increased automation, the manufacturing process for ring and pinion gears will continue to be optimized and improved to enhance production efficiency and product quality.